Polimer katkı maddeleri, temel polimerin fiziksel, kimyasal, proses veya optik özelliklerini iyileştirmek için az miktarda eklenen bileşiklerdir. Bu malzemeler, nihai ürünün performansını, dayanıklılığını ve işlenebilirliğini artırmada önemli bir rol oynar.
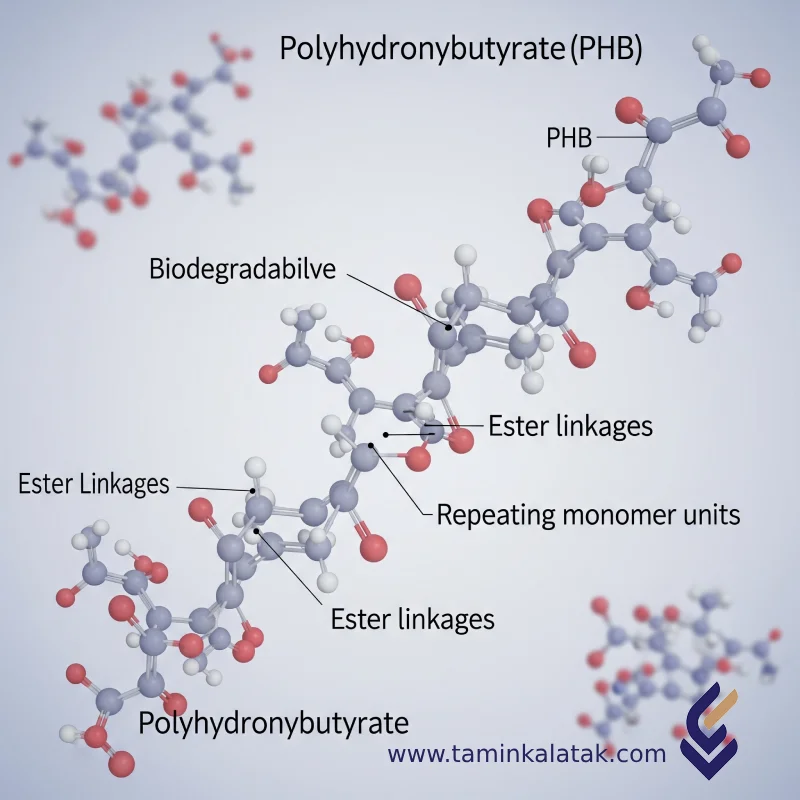
Polihidroksibutirat (PHB)
PHB is a biodegradable polyester with the chemical formula (C₄H₆O₂)ₙ.
It is synthesized by specific microorganisms under nutrient-limited conditions (such as nitrogen limitation).
Due to its high crystallinity (about 60–70%), PHB exhibits strength and rigidity comparable to polypropylene (PP).
However, unlike PP, PHB is fully biodegradable.
Its polymer chains are typically linear, and their mechanical properties depend on molecular weight and production conditions.
Properties of Polyhydroxybutyrate
-
Biodegradability: Completely decomposes in natural environments (soil, seawater, compost) through microbial activity.
-
Biocompatibility: Non-toxic and suitable for medical use.
-
Mechanical strength: Hardness and tensile strength comparable to conventional plastics like polypropylene.
-
Thermal resistance: Melting point between 160–180°C.
-
Renewable origin: Produced from biological sources such as glucose, agricultural waste, or vegetable oils.
Applications of Polyhydroxybutyrate
-
Packaging: Production of thin films, biodegradable bags, and disposable containers.
-
Medical field: Used in absorbable sutures, biocompatible implants, and drug-delivery systems.
-
Agriculture: Biodegradable mulching films and plant pots.
-
Textile industry: Production of fibers for sustainable fabrics.
-
Industrial products: Molded components for general applications.
Disadvantages of Polyhydroxybutyrate
Despite its many advantages, PHB also has some limitations:
-
High production cost: The microbial fermentation and extraction processes are expensive.
-
Brittleness: High crystallinity can lead to fragility in certain applications.
-
Variable degradation rate: In low-oxygen environments, biodegradation may proceed slowly.
-
Limited processability: High melting temperature and viscosity can complicate processing in some manufacturing methods.
Advantages of Polyhydroxybutyrate
-
Reduces plastic pollution: Fully biodegradable and decreases reliance on petroleum-based plastics.
-
Versatile applications: Suitable for use in medical, packaging, and agricultural industries.
-
Sustainable production: Can be derived from biomass and renewable resources.
-
High safety: Non-toxic and safe for food-contact applications.
Applications
Datasheets
PHB
| Products | Grid | Melt Flow Index (MFI) (g/10 min) | Density (g/cm³) | Process Method | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyethylene Furanoate (PEF) | PEF 100 | 2.0 - 3.5 | 138,00 | Injection Molding, Extrusion | Beverage bottles, food packaging |
| Polyethylene Furanoate (PEF) | PEF 200 | 4.0 - 5.0 | 137,00 | Blow Molding, Extrusion | Packaging films, industrial parts |
| Polyethylene Furanoate (PEF) | PEF 300 | 1.5 - 2.5 | 139,00 | Injection Molding | Electronics industries, automotive parts |